Gaskets 101: Types, Materials, and Uses in Industrial Applications
Introduction: The Role of Gaskets in Industrial Settings
Gaskets are essential in industrial operations, ensuring reliable seals in piping, machinery, and equipment. They prevent leaks, maintain pressure, and protect systems from contaminants. Whether in oil and gas, power generation, chemical processing, or water treatment, he right gasket selection is crucial for safety and efficiency.
This guide will help you understand different types of gaskets, their materials, and their industrial applications, with insights from Garlock, Durlon, Flexseal, Klinger, American Biltrite™, and other — trusted manufacturers in the sealing industry.
1. Types of Gaskets Used in Industrial Applications
Gaskets are categorized based on their material composition and intended application. The right choice depends on factors like pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure. Below are the three main types:
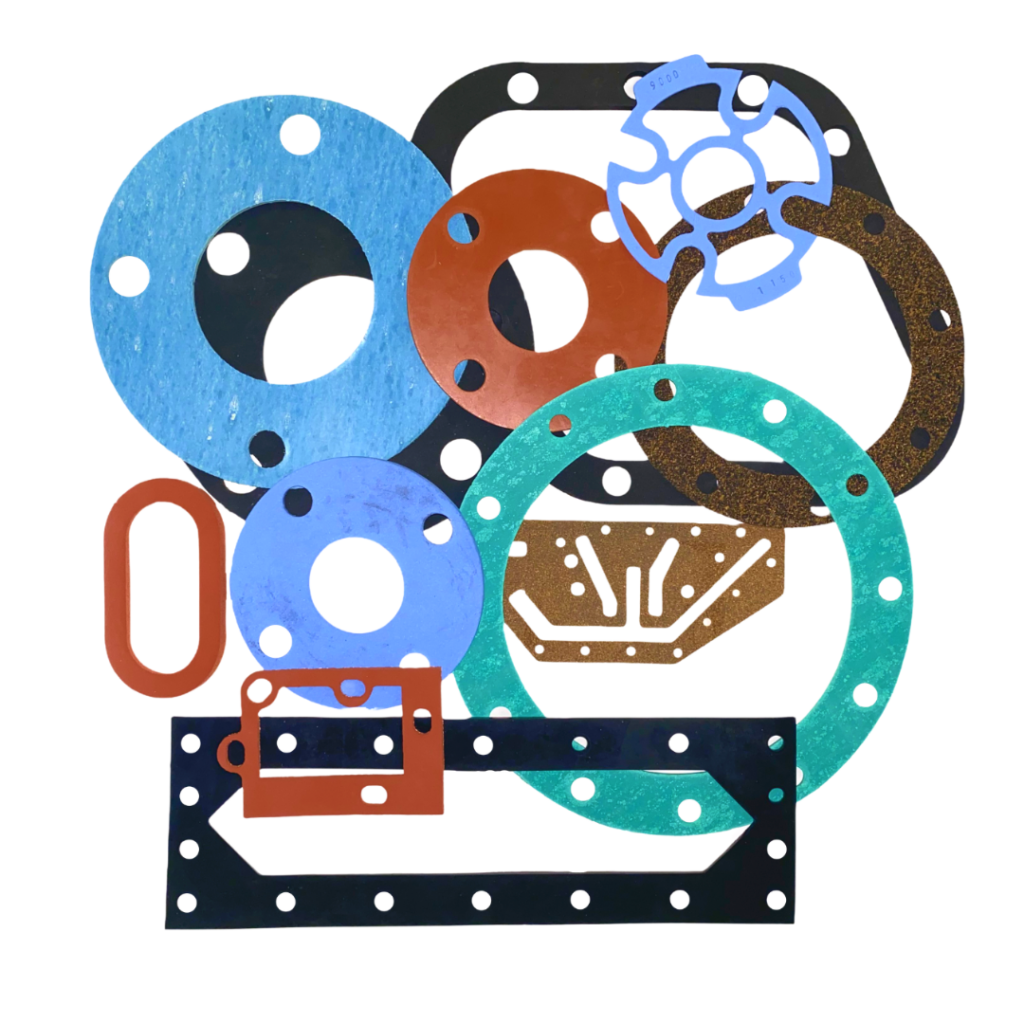
Soft (Non-Metallic) Gaskets – Made from rubber or elastomer, PTFE, or compressed fiber, these are flexible and best suited for low-pressure applications such as water systems, food processing, and chemical plants.
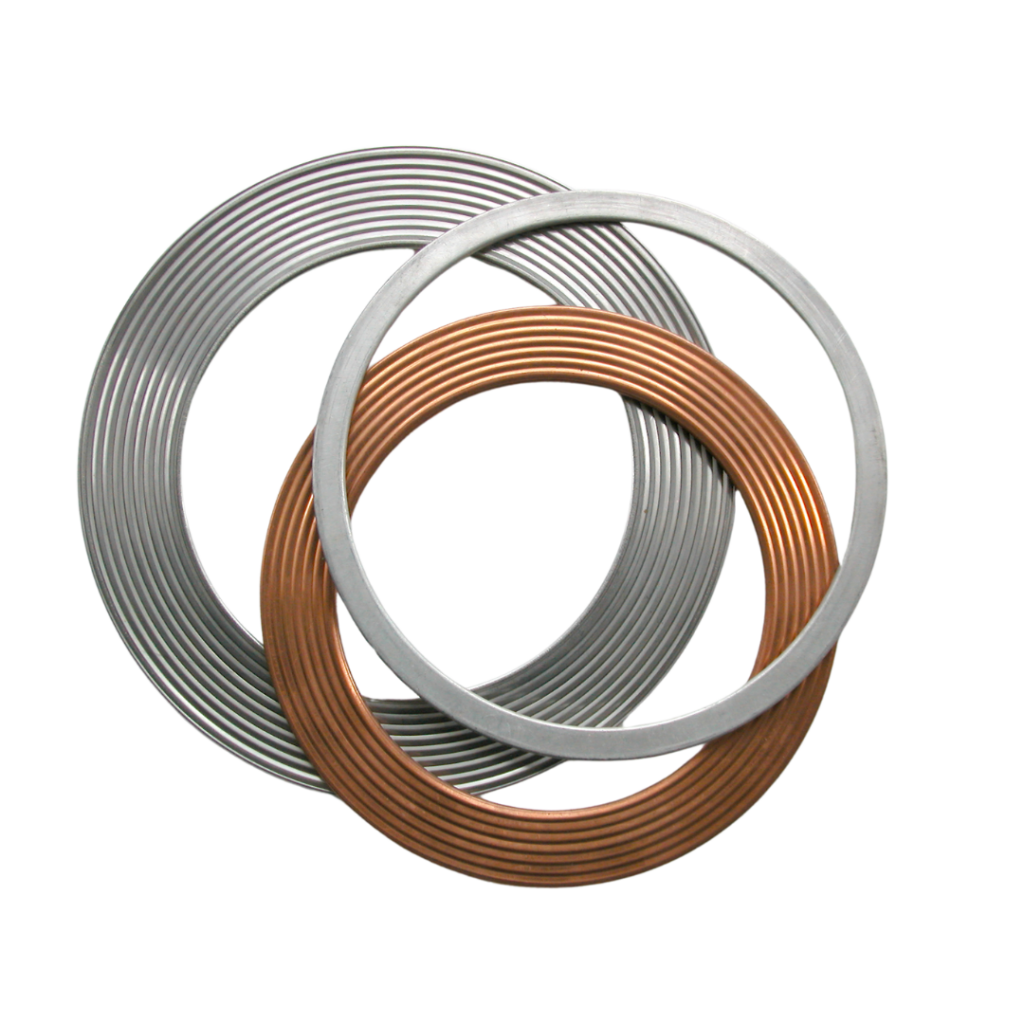

Metallic Gaskets – Made from solid metal (stainless steel, Inconel, copper), these are designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications such as steam systems, refineries, and power plants. Common examples include Ring-Type Joint (RTJ) gaskets, corrugated metal gaskets, and welded gaskets.
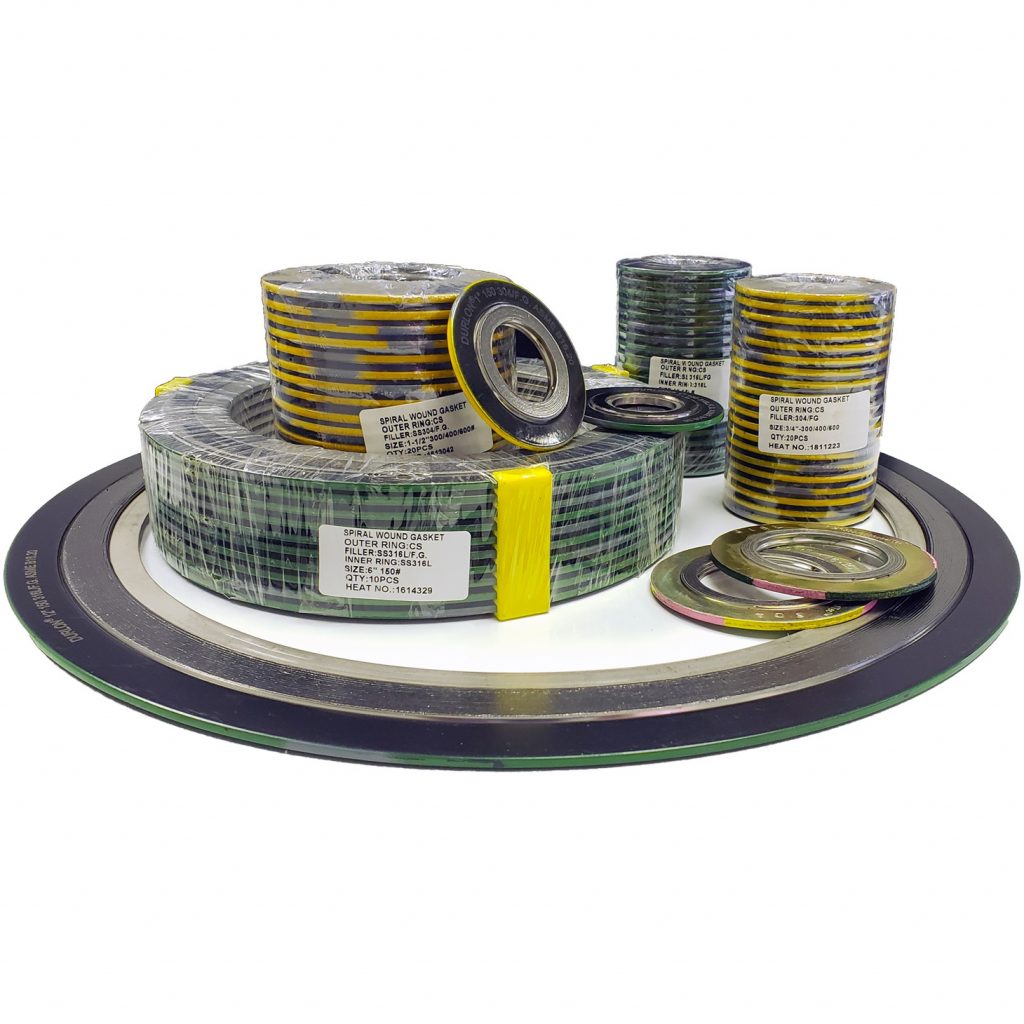

Semi-Metallic Gaskets – A combination of metal and non-metal materials, these gaskets offer durability and flexibility, making them ideal for heat exchangers, high-pressure pipelines, and industrial flanges. Examples include spiral wound gaskets, kammprofile gaskets, and metal-reinforced graphite gaskets.
2. Gasket Materials and Their Uses
Choosing the right material is crucial for gasket performance. The material must withstand factors like temperature, pressure, and exposure to chemicals. Below are some common gasket materials and their applications.
Material Key Benefits and Industries Used
Rubber (Nitrile, EPDM, Neoprene, Silicone)
- Flexible, water-resistant, and chemical-resistant.
- Water systems, HVAC, food processing.

- High chemical resistance, non-stick properties.
- Pharmaceutical, chemical plants.
- Withstands extreme heat and resists oxidation.
- Power plants, steam applications.

- High strength, long lifespan, and pressure-resistant.
- Oil & gas, high-pressure pipelines.

- Excellent for sealing against oils, fuels, and mild chemicals.
- Automotive, industrial machinery, chemical processing.

- High flexibility and vibration resistance.
- Automotive, transformers, low-pressure sealing.

3. How to Choose the Right Gasket
Selecting the right gasket is essential for preventing leaks and ensuring the longevity of industrial systems. The selection process depends on multiple factors, including temperature, pressure, chemical compatibility, and mechanical load. Below are the key considerations:

1. Temperature and Pressure Compatibility
- Low-pressure applications: Soft gaskets such as rubber or compressed fiber are ideal.
- High-pressure environments: Metallic gaskets, like RTJ and corrugated metal gaskets, are necessary for durability and stability.

2. Chemical Compatibility
- Aggressive chemical environments: PTFE (Teflon) offers the best resistance.
- Oil and fuel applications: Nitrile rubber gaskets provide effective sealing.
- Steam and high-temperature applications: Graphite-based gaskets ensure longevity.
3. Flange Surface and Load
- Irregular flange surfaces: Soft gaskets such as compressed fiber sheets work best.
- High bolt load applications: Metallic gaskets require precise torqueing and load distribution.
- Misaligned flanges: Semi-metallic gaskets offer a balance of flexibility and durability.

4. Industry Standards and Certifications
- NSF-61 certification: Required for potable water applications.
- API 6A standard: Specifies requirements for oil and gas industry gaskets.
- ASME B16.20 standard: Governs metallic and spiral wound gasket design.
- FDA compliance: Required for food and pharmaceutical applications.
4. Installation Best Practices for Industrial Gaskets
Proper installation is just as important as material selection. A poorly installed gasket can lead to leaks, pressure loss, and even system failure. Following these best practices ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Key Steps for Proper Installation:
Inspect the flange and gasket – Ensure the flange surface is clean, dry, and free of debris before installation.
Align the gasket properly – The gasket should sit evenly on the sealing surface without being forced into place.
Use the correct torque sequence – Bolts must be tightened gradually and evenly using a cross-pattern method to avoid uneven pressure.
Avoid over-tightening – Excessive torque can damage soft gaskets or deform metallic ones. Follow manufacturer torque guidelines.
- Consider lubrication – Using a non-contaminating lubricant on bolt threads can ensure even torque application.
Facts You Might Not Know About Industrial Gaskets
Beyond their basic function, gaskets have unique characteristics that can impact performance. Here are some key facts that are often overlooked:
According to Durlon, temperature fluctuations can weaken gaskets over time.
Garlock’s research shows that improper bolt tightening causes 80% of gasket failures.
UV exposure weakens rubber gaskets. American Biltrite™ notes that rubber-based gaskets exposed to sunlight for prolonged periods degrade faster.
Certain gaskets require re-tightening after system pressurization to maintain their seal.
Material selection can impact energy efficiency, as some gaskets reduce heat loss better than others.
Using the wrong gasket can lead to leaks, equipment damage, and increased maintenance costs. Take note that proper gasket selection and installation ensure optimal performance, minimize downtime, and extend equipment life.
For high-quality gaskets tailored to industrial applications, check out Custom Gaskets Ltd.’s product selection for solutions designed to meet industry standards.
